
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | |
Integration |
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
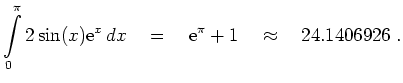
Trapezregel:
>> % Integrationsdaten
>> x=[ 0 .2 .4 .6:.1:1 ]*pi;
>> y=2*sin(x).*exp(x);
>> % relativer Fehler Trapezregel (rund 1%)
>> F=trapz(x,y)
F =
23.9117
>> exakt=exp(pi)+1;
>> e=abs(F-exakt)/exakt
e =
0.0095
![\includegraphics[width=.7\linewidth]{quad}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel225/img2.png)
Integrationsmethoden höherer Ordnung:
>> % relativer Fehler Simpson adaptiv
>> F=quad('2*sin(x).*exp(x)',0,pi)
F =
24.1407
>> e=abs(F-exakt)/exakt
e =
3.4291e-10
>> % relativer Fehler Lobatto adaptiv
>> F=quadl('2*sin(x).*exp(x)',0,pi)
F =
24.1407
>> e=abs(F-exakt)/exakt
e =
1.0743e-14
2D-Integration: Bestimmung der Fläche des Einheitskreises durch Integration der charakteristischen Funktion

>> % Integration und relativer Fehler
>> F=dblquad('x.^2+y.^2<=1',-1,1,-1,1)
F =
3.1416
>> e=abs(F-pi)/pi
e =
5.9949e-06
| automatisch erstellt am 25. 1. 2006 |