
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |

|
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | ||
Fourier-Basis | ||
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
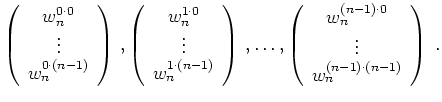
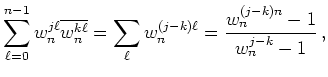
Für ![]() ist
ist
![]() ,
und man erhält die Basisvektoren
,
und man erhält die Basisvektoren
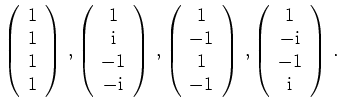
siehe auch:
| automatisch erstellt am 19. 8. 2013 |