
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | |
Integration mit Maple |
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
> int(sin(x)^2, x=0..Pi);
> int(sin(x)^2, x);
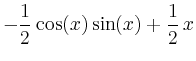
Kann MAPLE für die Funktion keine Stammfunktion finden, so wird einfach der eingebene Ausdruck ausgegeben, man kann jedoch bestimmte Integrale numerisch berechnen lassen, indem man den Befehl evalf auf den Integral-Operator Int anwendet.
> int(exp(x^3), x=0..2);
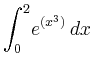
> evalf( Int(exp(x^3), x=0..2) );
Einige Beispiele zur Bildung von Stammfunktionen in Maple sind:
> int(sin(x)^2*cos(x)^4,x);
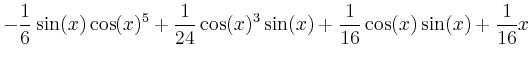
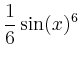
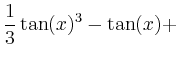 arctan
arctan
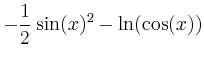
| automatisch erstellt am 5. 3. 2012 |