
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | |
Länge von Kurven |
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
Berechne jeweils die Länge der Kurve ![]() .
.
Lösung.
![$\displaystyle \ell(\gamma)
\;=\; \int_0^1 \left\Vert\dot{\gamma}(t)\right\Vert\...
...2)\;\mathrm{d}t
\;=\; \left[t+\frac{2}{3}\;t^3\right]_0^1
\;=\; \frac{5}{3}\;.
$](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel1139/img13.png)
Skizze.
![\includegraphics[width = 8cm]{l1-1.eps}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel1139/img14.png)
![\begin{displaymath}
\begin{array}{rcl}
\ell(\gamma)
&=& \displaystyle\int_0^{2\p...
...frac{t}{2}\right]_0^{2\pi}\vspace*{2mm}\\
&=& 8\;.
\end{array}\end{displaymath}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel1139/img15.png)
Dabei haben wir folgende Identität verwendet.
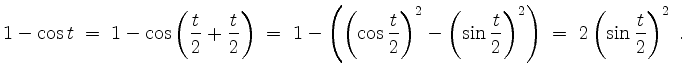
Skizze.
![\includegraphics[width = 8cm]{l1-2.eps}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel1139/img17.png)
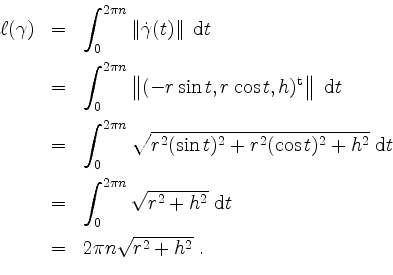
Skizze für ![]() ,
, ![]() und
und ![]() .
.
![\includegraphics[width = 8cm]{l1-3.eps}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel1139/img22.png)
siehe auch:
| automatisch erstellt am 11. 8. 2006 |