Varianten für die Eingabe einer
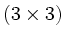 -Matrix:
-Matrix:
>> A=[1,2,3;4,5,6;7,8,9]
A =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
>> A=[1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9]
A =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
Beispiel für die Fortsetzung von Eingabezeilen mit Hilfe von Fortsetzungspunkten:
>> B=[ 1 2 3 4 ...
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12 ...
13 14 15 16]
B =
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Fortsetzungspunkte, Zeilenschaltungen, Kommas und Strichpunkte lassen sich bei
der Definition von Matrizen beliebig kombinieren. Zudem können auch komplexe
Matrixelemente verwendet werden:
>> C=[-i,2+3i,0
-inf 1+2 ...
17; 2^2 1 -3i]
C =
0 - 1.0000i 2.0000 + 3.0000i 0
-Inf 3.0000 17.0000
4.0000 1.0000 0 - 3.0000i
Matrizen, Vektoren und Skalare zählen in MATLAB zur Speicherklasse
double array:
>> v1=[1,2,3]
v1 =
1 2 3
>> v2=[1;2;3]
v2 =
1
2
3
>> [2]-2
ans =
0
>> whos
Name Size Bytes Class
A 3x3 72 double array
B 2x8 128 double array
ans 1x1 8 double array
v1 1x3 24 double array
v2 3x1 24 double array
(Autoren: Hörner/Wipper)
| |
automatisch erstellt
am 12. 1. 2007 |

