
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |

|
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | ||
Beispiel: Produktregel | ||
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
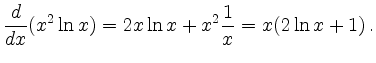
![$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx} \left[ \sin x (x^2 \ln x )\right] = \cos x (x^2 \ln x) + \sin x (x(2 \ln x + 1)) \,.
$](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel296/img3.png)
![$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx} \left[ \sin x (x^2 \ln x) \right] = \cos x (x^2 \ln x) + 2x (\sin x \ln x) + \frac{1}{x} (\sin x\, x^2 )\,.
$](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel296/img4.png)
| automatisch erstellt am 18. 9. 2007 |