
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | |
Faltungsformel |
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
Verifiziere die Faltungsformel
![]() .
.
Verwende die Faltungsformel zur Berechnung von
![]() . Berechne zur Probe direkt.
. Berechne zur Probe direkt.
Mit Hilfe der Substitution
![]() folgt die Faltungsformel
folgt die Faltungsformel
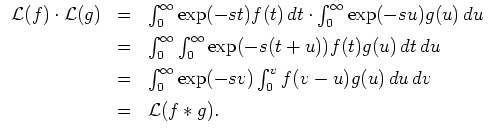
Sei
![]() , sei
, sei
![]() , und sei
, und sei
![]() . Zu berechnen ist
. Zu berechnen ist
![]() .
.
Es wird
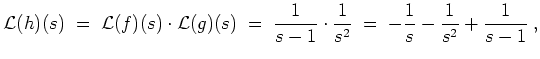
Direkt wird
![$ \mbox{$\displaystyle
\int_0^1 \exp(1-u)\cdot u \, du\; =\; [-\exp(1-u)\cdot u]_0^1 +\int_0^1 \exp(1-u)\, du \;= \; -1 + [-\exp(1-u)]_0^1\; =\; e - 2\; .
$}$](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel482/img12.png)
siehe auch:
| automatisch erstellt am 25. 1. 2006 |