
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |

|
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | ||
Mercator-Projektion | ||
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
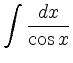
läßt sich mit der Substitution
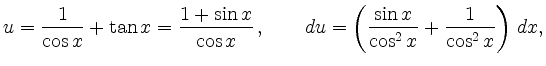
berechnen:
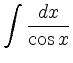 |
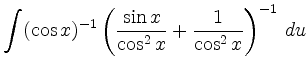 |
||
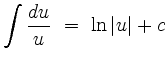 |
|||
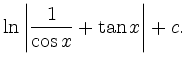 |
Eine Anwendung ist die Mercator-Projektion. Hierbei wird die Erdoberfläche winkeltreu auf eine Ebene projiziert.
![\includegraphics[height=3cm]{bsp_mercator_bild1.eps}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel92/img7.png) |
![\includegraphics[height=3cm]{bsp_mercator_bild2.eps}](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel92/img8.png) |
Die Breitenkreise werden dabei mit dem Verhältnis
![]() gestreckt.
gestreckt.
siehe auch:
| automatisch erstellt am 8. 4. 2008 |