
Mathematik-Online-Aufgabensammlung: Lösung zu

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Aufgabensammlung: Lösung zu | |
Aufgabe 1277: Grenzwerte bestimmen. |
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
![$\displaystyle \begin{array}{lll}
{\bf {a)}} \quad {\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 0}\...
...f)}} \quad {\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 0+0}\ \sqrt[x]{1+\sinh{x}}}}
\end{array} $](/inhalt/aufgabe/aufgabe1277/img1.png)
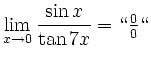
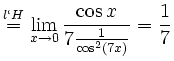
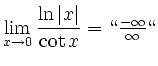
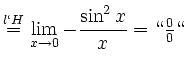
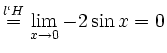
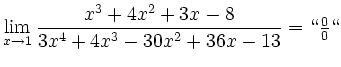
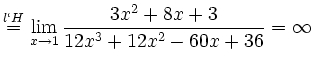
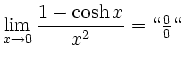
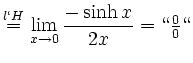
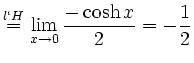
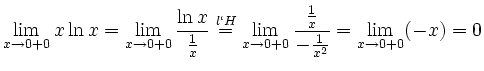
![$\displaystyle \sqrt[x]{1+\sinh x} = (1+\sinh x)^\frac{1}{x} = e^{\frac{\ln(1+\sinh x)}{x}}$](/inhalt/loesung/loesung621/img14.png)
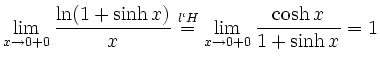
| automatisch erstellt am 20. 6. 2006 |