
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon:

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Lexikon: | |
Beispiel: Univariate Fourier-Transformation |
| A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z | Übersicht |
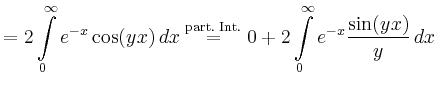 |
||
![$\displaystyle \overset{\text{part. Int.}}{=} 2\left[e^{-x}\left(-\frac{\cos(yx)...
...}\right)\right]_0^\infty - 2\int\limits_0^\infty e^{-x}\frac{\cos(yx)}{y^2}\,dx$](/inhalt/beispiel/beispiel744/img7.png) |
||
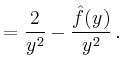 |
||
|
Aufgelöst ergibt sich
| ||
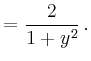 |
||
| automatisch erstellt am 13. 11. 2013 |