
Mathematik-Online-Kurs: Formelsammlung - Analysis einer Veränderlichen

|
[Home] [Lexikon] [Aufgaben] [Tests] [Kurse] [Begleitmaterial] [Hinweise] [Mitwirkende] [Publikationen] |
|
Mathematik-Online-Kurs: Formelsammlung - Analysis einer Veränderlichen | |
Funktionen |
| [vorangehende Seite] [nachfolgende Seite] | [Gesamtverzeichnis][Seitenübersicht] |
| Exponentialfunktion |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithmen |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trigonometrische Funktionen | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hyperbelfunktionen |
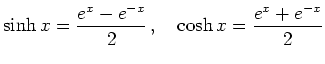
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [vorangehende Seite] [nachfolgende Seite] | [Gesamtverzeichnis][Seitenübersicht] |
| automatisch erstellt am 31.1.2006 |